FUNCTIONALITY OF AIR CONDITIONERS.
Air conditioners have a complex functionality that involves multiple components and processes working together to cool and dehumidify the air in a room or an enclosed space. By combining these components and processes, air conditioners effectively cool and dehumidify the air in a space, providing comfort and maintaining indoor temperature and humidity levels. Below is a detailed overview of the functionality of air conditioners:
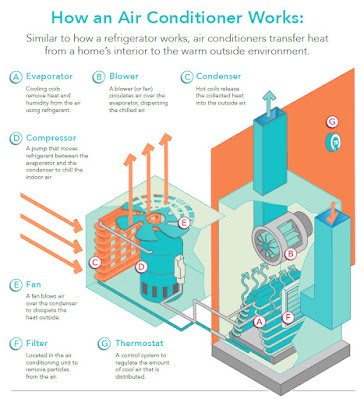
Refrigerant
Air conditioners use a refrigerant, a specialized chemical compound that undergoes a continuous cycle of evaporation and condensation to absorb and release heat. The most commonly used refrigerants are hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) or hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs).
Compressor
The refrigeration process starts with the compressor. The compressor's main function is to compress the refrigerant, raising its temperature and pressure. By compressing the refrigerant, the compressor causes its molecules to move closer together, resulting in increased energy.
Condenser
After leaving the compressor, the high-pressure, high-temperature refrigerant moves into the condenser. The condenser consists of coiled tubes and fins that help dissipate heat. As the refrigerant flows through the condenser, it releases heat to the surroundings, typically through the outdoor unit of the air conditioner.
Expansion valve
The expansion valve is a small throttling device located between the condenser and the evaporator coil. Its function is to regulate the flow of high-pressure liquid refrigerant into the evaporator coil. As the refrigerant passes through the expansion valve, its pressure decreases dramatically, resulting in rapid expansion and cooling.
Evaporator coil
The low-pressure, low-temperature refrigerant now enters the evaporator coil, which is located inside the indoor unit of the air conditioner. The evaporator coil consists of numerous small tubes that provide a large surface area for heat exchange. As warm air from the room is blown across the evaporator coil, the cold refrigerant absorbs heat, thereby cooling the air.
Blower fan
The blower fan, situated inside the indoor unit, circulates the cooled air from the evaporator coil into the room. It also helps maintain a steady airflow, ensuring that air reaches each corner of the space.
Dehumidification
As the warm air passes over the evaporator coil, the humidity in the air condenses on the cold surface of the coil, leading to dehumidification. The condensed moisture drips into a collection pan or is drained out of the system through a designated outlet.
Thermostat and control system
Air conditioners are typically equipped with a thermostat and a control system. The thermostat allows users to set and maintain the desired temperature. The control system monitors the temperature in the room and adjusts the operation of the compressor, blower fan, and other components to maintain the set temperature.
Air filters
Air conditioners often include air filters to improve indoor air quality by capturing dust, pollen, pet dander, and other airborne particles. These filters need regular cleaning or replacement to maintain their effectiveness.
Dual-mode functionality
Some air conditioners offer dual-mode functionality, providing both cooling and heating capabilities. In such units, the refrigeration cycle can be reversed, allowing the air conditioner to function as a heater by extracting heat from the outdoor air and releasing it indoors.
Cooling Mechanism
Air conditioners work by removing heat and humidity from the air in a space, using a refrigeration cycle. They circulate refrigerant between an indoor and outdoor unit, absorbing heat from indoor air and releasing it outdoors.
Types of Air Conditioners
There are various types of air conditioners available, including window units, split-systems, portable units, and central air conditioning systems. Each type has its own installation requirements and cooling capacities.
Energy Efficiency
Air conditioners are labeled with an Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER) or Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio (SEER), which indicate their energy efficiency. Higher EER or SEER ratings mean the unit consumes less energy to provide cooling and is more environmentally friendly.
Maintenance
Regular maintenance is crucial for optimal performance and longevity of air conditioners. This includes cleaning or replacing filters, checking refrigerant levels, inspecting and cleaning coils, and ensuring proper airflow.
Thermostat Settings
Properly setting the thermostat is important for energy efficiency and comfort. Setting the desired temperature too low may lead to excessive energy consumption. It is generally recommended to set the thermostat between 72-78°F (22-26°C) for optimal comfort and efficiency.
Indoor Air Quality
Air conditioners can help improve indoor air quality by filtering out dust, pollen, and other airborne particles. However, it's important to regularly clean or replace filters to maintain optimal air quality.
Sizing the AC
Choosing the right size air conditioner for your space is essential. An undersized unit may struggle to cool the area, while an oversized unit can lead to inefficient cooling and increased energy consumption.
Noise Levels
Air conditioners produce varying levels of noise during operation. If noise is a concern, it's advisable to choose air conditioners with low noise ratings or opt for split-system units where the noisy components are placed outside.
Inverter Technology
Inverter air conditioners adjust the compressor speed based on cooling requirements, resulting in more precise and efficient cooling. While they may have higher upfront costs, they can save energy and provide better temperature control in the long run.
Environmental Impact
The refrigerants used in air conditioners can have an impact on the environment. Older units may use refrigerants that contribute to ozone depletion or have high global warming potentials. Newer models often utilize more environmentally friendly refrigerants, such as R-410A or R-32.
Conclusion
Understanding these key aspects of air conditioners can help you make informed decisions when selecting, operating, and maintaining your cooling system, ensuring optimal comfort and efficiency in your living or working space.


Comments
Post a Comment